Introduction to GuardDuty Malware Protection
In today’s landscape of escalating frequency, scale and complexity of attacks it’s important to use every tool at your disposal to increase your defenses and decrease your attack footprint. AWS has stepped up previously with services such as GuardDuty, Security Hub, and Inspector. GuardDuty provides intelligent threat detection by monitoring your accounts for malicious activity. Now we have a powerful new addition to Guard Duty’s functionality: Guard Duty Malware Protection! This service automatically triggers on detection of possibly compromised EC2 instances based on leading indicators identified by GuardDuty. Upon triggering, GuardDuty’s compute then scans the affected resource for malware. The service detects malware on both EC2 Instances and containers. No additional software installation is required, and system performance is not affected by this service. There are also protections available for ECS and Kubernetes. In order to use it, the feature must be enabled in GuardDuty (and can be enabled across your AWS Organization!).
In order for GuardDuty to scan for malware and not affect performance, GuardDuty creates a snapshot of the EBS volumes attached to the instance and replica EBS volumes are created in the GuardDuty account to scan. The replica volumes are automatically deleted once the scan is done. If GuardDuty detects malware on the instance, a new finding is generated with details and location.
Features
- No additional software installation is required
- Does not affect system performance
- You can enable or disable malware protection for any account, or region, at any time
- Works for EBS-backed EC2 instances, ECS, and Kubernetes
Setup of the Service
I’m happy to report that setting up the service is as simple as checking some boxes. The service can be setup in a single account or via AWS Organizations. If taking this approach, single or multiple accounts can be added. When working with AWS Organizations, the administrator can configure malware scanning for all member accounts. The member accounts will then follow the parent account settings. Member accounts cannot modify settings for this feature from their console. You can choose to have malware scanning turned on for all existing and new accounts in the organization. Alternatively, selective accounts can be turned on for this feature.
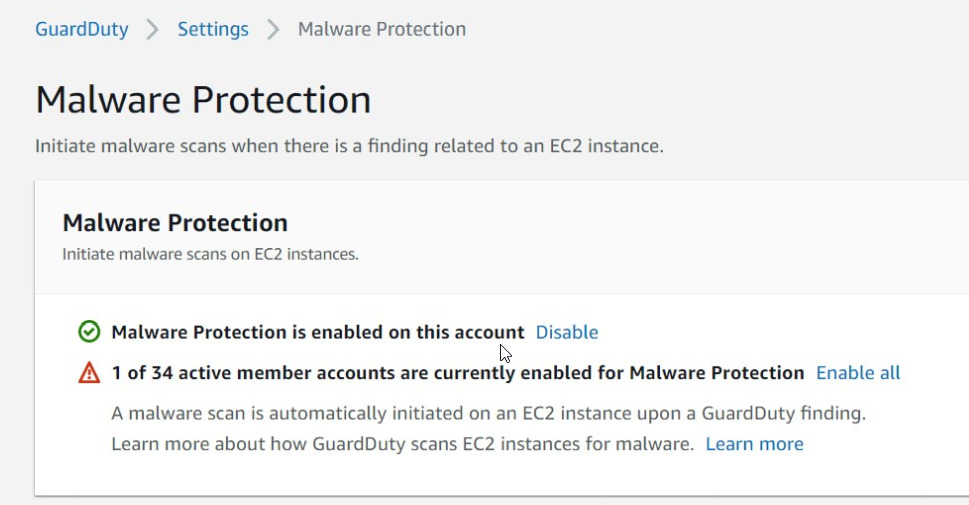
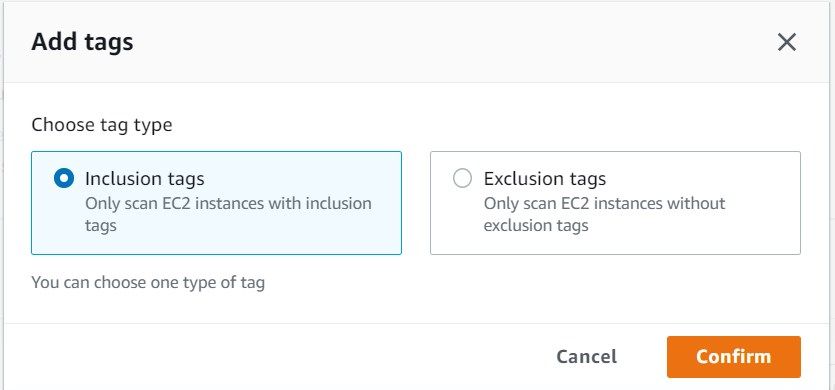
Additionally, inclusion or exclusion tags can be used to further refine what gets scanned. If using inclusion tags, only the instances with the inclusion tag will be scanned. For exclusion tags, only the instances without exclusion tags will be scanned. The mechanism to accomplish this is via tags. The GuardDuty console allows you to go straight to a manage tags screen to filter your malware scanning.
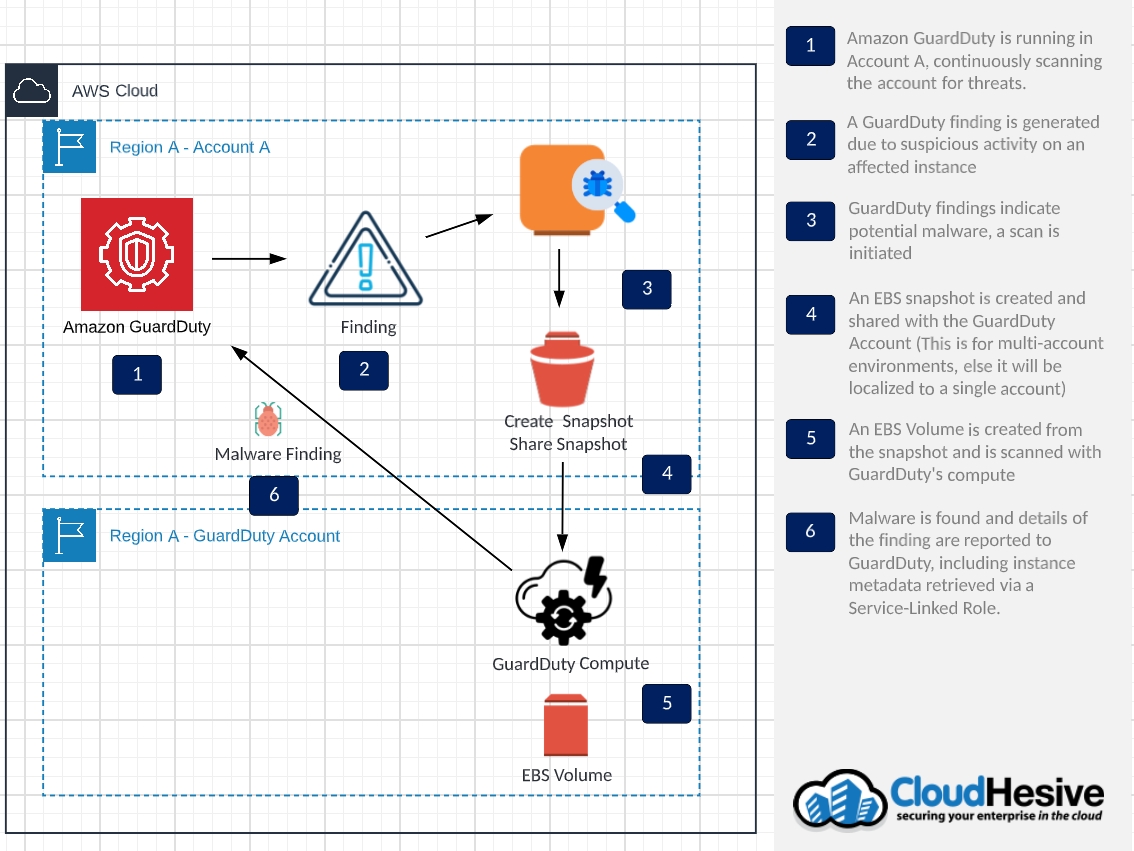
How it Works
Essentially – the flow goes as follows: GuardDuty findings trigger a scan, then the scan reports the findings and results via GuardDuty, which you can process manually or via EventBridge. When GuardDuty detects an instance exhibiting suspicious behavior, this finding will trigger a malware scan of the instance or container. Before beginning the scan, GuardDuty will take a snapshot of the affected EBS volume, create a new volume from the snapshot, and then scan it utilizing GuardDuty’s compute. The snapshot is tagged with a key of GuardDutyCreated and a value of true. Once the scan is completed, the findings are published and the replica volume and snapshot are deleted. This ensures isolation and not impacting the performance of the affected instance. Aside from the details available in the GuardDuty console, a CloudWatch log is also added under the log group: /aws/guardduty/malware-scan-events. This contains the triggering findings and scan details.
Additionally, for the snapshot process the EBS volume must be 1TB or smaller. Regarding encryption – GuardDuty will scan volumes that are unencrypted with its own key to scan the volumes. If you are using a customer managed KMS key, the same key will be used for the replica volumes. If EBS encryption is used, the volume will not be scanned. For permissions, a service-linked role is used for EBS access and metadata retrieval used in reporting findings.
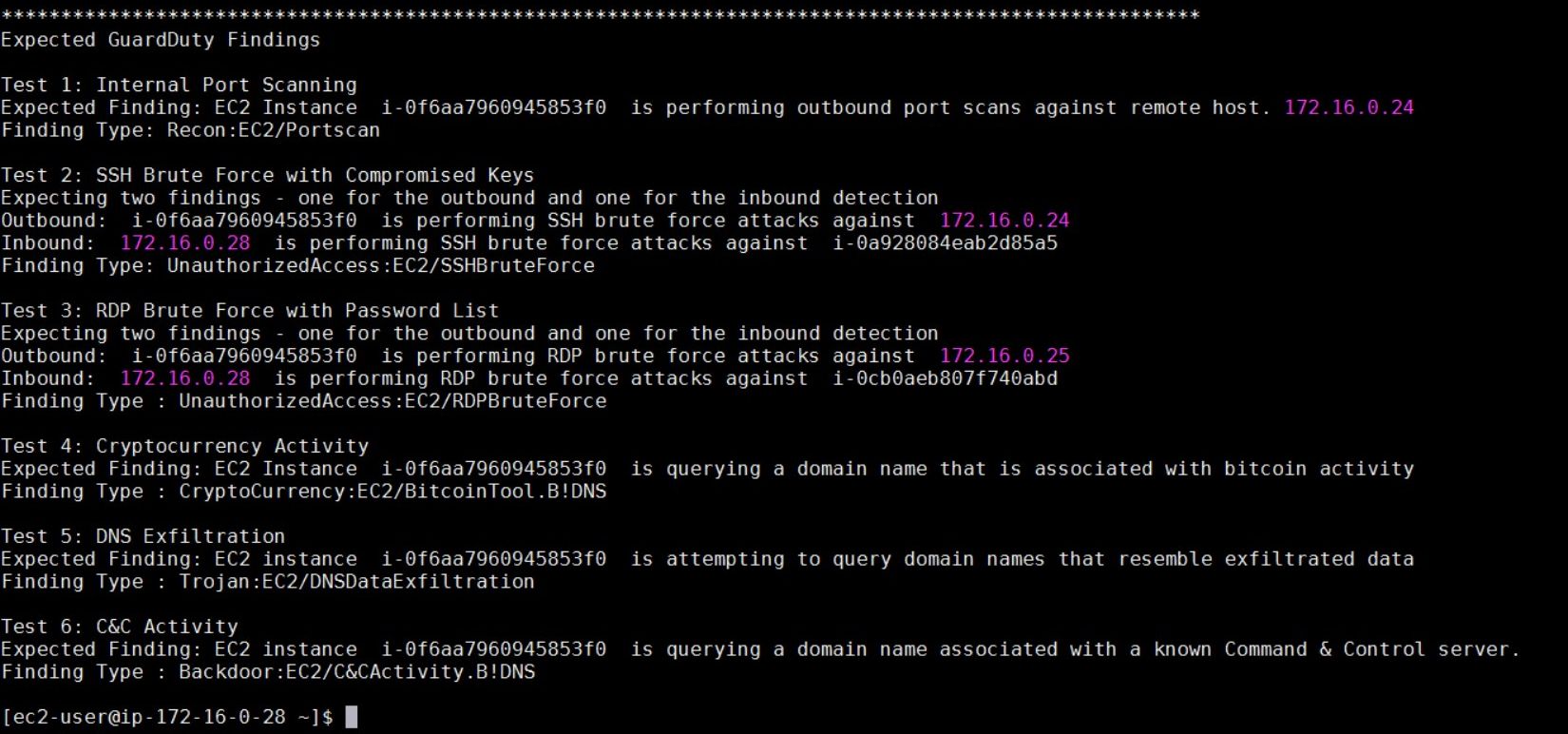
Some of the examples of triggering behavior are shown here:
Testing and Validation
The new findings that you will see in GuardDuty Malware Protection are of the category ‘Execution’ and value of Malicious or Suspicious File. These GuardDuty Findings occur for EC2, ECS, Container, and Kubernetes.
Findings for MaliciousFile indicate that malware was found on the instance. Remediation should follow either manually or via integration \ automation through your security information and event management solution (SIEM). Findings for SuspiciousFile mean that while malware may not have been found, files which contain adware, spyware, or dual use tools have been found. It is recommended to review the findings and see whether those files or tools are legitimate. For example, network scanning tools can be used for legitimate purposes or for attack scanning.
What the Result Looks Like
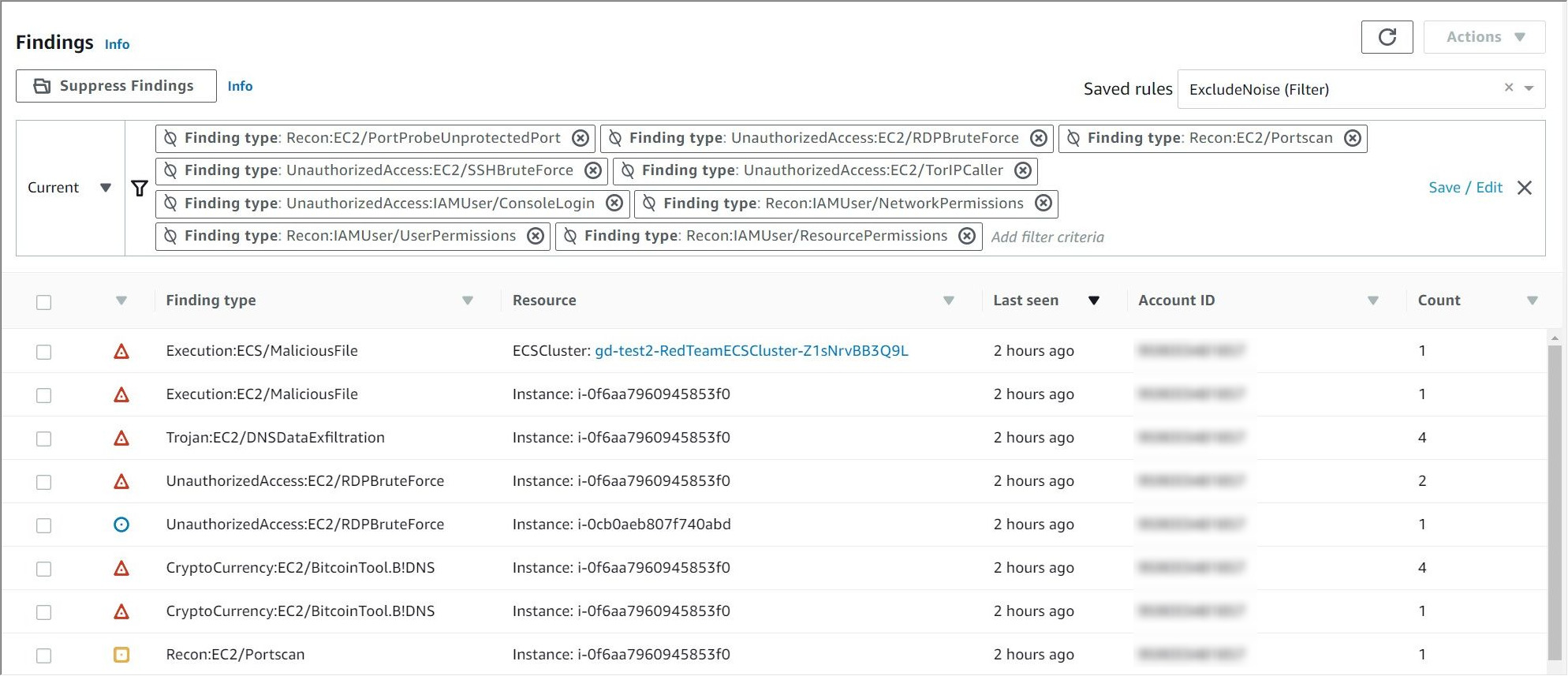
The results below are show the findings demonstrating Malicious File detection, DNS Data Exfiltration, Brute Force attacks and Bitcoin mining tools.
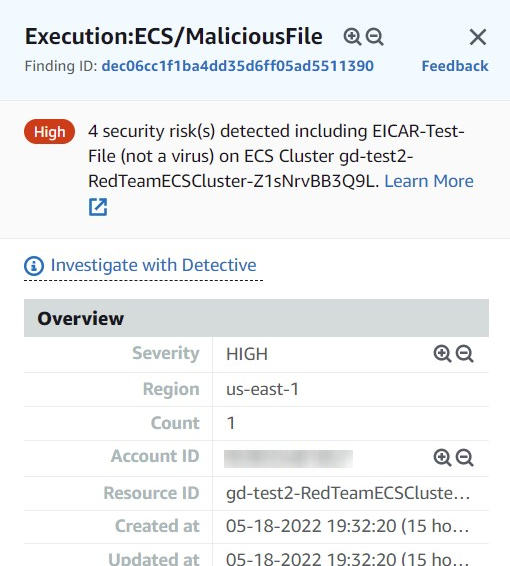
Looking at the first result, the details are shown here for malicious file on an ECS Cluster.
Service Value
GuardDuty Malware Protection provides additional value to organizations and coexists with other anti-malware solutions, increasing an organization’s security posture through defense in depth. This defense in depth provides protection where the installation of a software agent may be infeasible, or there may be performance concerns. Further, there may be situations in which there are unintended gaps of your agent based antimalware solution – due to gaps in configuration management, change management automation, or even cases of more aggressive malware actively seeking and disabling software based solutions. Finally, GuardDuty Malware Protection is priced using a consumption based model typical of cloud services, which scales with your organization.
Extensibility
For those familiar with GuardDuty, GuardDuty findings are emitted via Event Bridge, which creates immense capabilities when it comes to integration with other systems and organizational processes. Much like GuardDuty, GuardDuty Malware Protection also emits events via Event Bridge, which allows sending of findings (or lack thereof) to Service Management (ticketing) systems, Escalation systems, SIEMs or even invoke automated response and recovery playbooks.
Extensibility and automation is crucial to ensuring the consistently applied response to a finding, measurement of response to findings and, by leveraging automation in the response and recovery to a finding, an instance can be isolated/destroyed and (optionally) it’s memory and storage can be captured for forensic purposes without the need for human intervention.
Conclusion
GuardDuty Malware Protection is a natural extension to GuardDuty as a common step upon identification of leading indicators of malware is to positively identify the presence malware stored or running in associated compute environments. It’s integration with other AWS services, and extensibility via Event Bridge serve to make implementation and integration a straight forward exercise with measurable value to your organization’s security posture.
-Jorge Rodriguez, Senior Lead Cloud Engineer, CloudHesive and Patrick Hannah, CTO, CloudHesive


